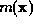 , which may represent a molecular envelope or some other prior
information. Let the desired distribution be
, which may represent a molecular envelope or some other prior
information. Let the desired distribution be 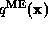 , whose
Fourier coefficients are
, whose
Fourier coefficients are 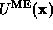 .
.

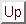

We require the maximum entropy probability distribution consistent
with a set of structure factor constraints and some prior probability
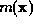 , which may represent a molecular envelope or some other prior
information. Let the desired distribution be
, which may represent a molecular envelope or some other prior
information. Let the desired distribution be 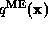 , whose
Fourier coefficients are
, whose
Fourier coefficients are 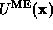 .
.
If M structure factors are known both in magnitude and phase, these may be expressed as complex constraints of the following form
where 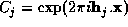 ,
, 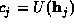 . We include the origin term with j=0,
. We include the origin term with j=0, 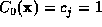 .
.
We must find the function 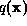 consistent with the constraints
(6) for which the entropy
consistent with the constraints
(6) for which the entropy 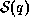 is a maximum. Using the method
of Lagrange multipliers, this is equivalent to the unconstrained
maximisation of the function
is a maximum. Using the method
of Lagrange multipliers, this is equivalent to the unconstrained
maximisation of the function
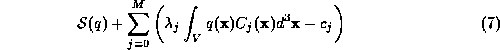
with respect to 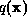 ,
, 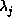 .
.
Differentiating with respect to the 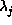 returns the constraint
equations (6), while differentiating with respect to
returns the constraint
equations (6), while differentiating with respect to
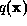 yields the equations:
yields the equations:
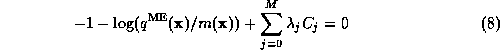
or:
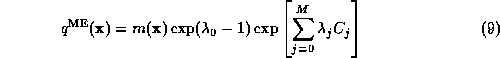
We may solve for 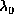 directly by integrating this equation
over
directly by integrating this equation
over  and using
and using 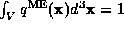 (constraint 0):
(constraint 0):
Then:
Equations (11), (12), and (13) are the
maximum entropy equations. These must be solved for the Lagrange
multipliers 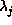 , and thus determine the maximum entropy
distribution
, and thus determine the maximum entropy
distribution 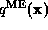 .
.