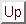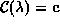 can be solved for
can be solved for  by
the Newton Raphson method. Some initial estimate
by
the Newton Raphson method. Some initial estimate 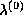 is
iteratively improved according to the formula
is
iteratively improved according to the formula

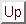

The set of equations 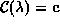 can be solved for
can be solved for  by
the Newton Raphson method. Some initial estimate
by
the Newton Raphson method. Some initial estimate 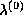 is
iteratively improved according to the formula
is
iteratively improved according to the formula
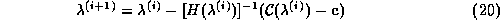
where H is the Hessian matrix of the constraint equations:
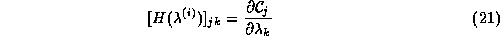
In the case of the maximum entropy equations (11), (12) and (14), this matrix is given by equation (16), i.e.
where  are the Fourier coefficients of
are the Fourier coefficients of  , which is
calculated as in (12):
, which is
calculated as in (12):
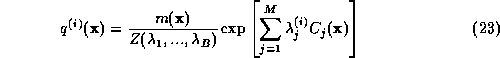
Since  for large M, the first term in equation
(22) will tend to dominate. In this case, the matrix reduces to the
Karle-Hauptman matrix of the current estimate of the probability
density. The inverse of the Hessian will then be approximately the
Karle-Hauptman matrix of the reciprocal of the estimated probability
density (appendix A). Thus we can write
for large M, the first term in equation
(22) will tend to dominate. In this case, the matrix reduces to the
Karle-Hauptman matrix of the current estimate of the probability
density. The inverse of the Hessian will then be approximately the
Karle-Hauptman matrix of the reciprocal of the estimated probability
density (appendix A). Thus we can write
where 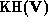 is the Karle-Hauptman matrix of
is the Karle-Hauptman matrix of 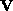 ,
the vector of coefficients of the inverse density:
,
the vector of coefficients of the inverse density:
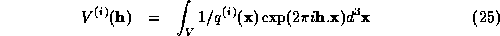
Expanding equation (24) for individual terms, we get:

In the case where the constraint equations are contain the values of a
subset of the complex structure factors, the coefficients 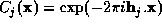 . In this case the solution of the
maximum-entropy equations by exponential modelling is performed as
follows:
. In this case the solution of the
maximum-entropy equations by exponential modelling is performed as
follows:
Note that Fourier transforms are present in equations (26)-(31). In equations (26) and (29) where the summation is performed in reciprocal space, only those terms for which reflections are constrained are included.
If other linear constraints are imposed upon the probability density, then the summations can no longer be performed by Fourier transform and the additional constraints must be included by direct summation. The Hessian matrix must also be suitably modified.
Bricogne notes that the algorithm is unstable, with the division in
(30) leading to a rapidly increasing dynamic range in
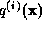 . He suggests that shifts should be applied to
. He suggests that shifts should be applied to
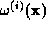 along two directions; one given by
along two directions; one given by
 to satisfy the constraints, and the other by
to satisfy the constraints, and the other by
 to oppose the buildup of contrast in
to oppose the buildup of contrast in
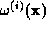 (Bricogne, 1990). This scheme convergences in
10-20 cycles.
(Bricogne, 1990). This scheme convergences in
10-20 cycles.