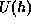 can be defined as follows,
can be defined as follows,

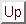

The Karle-Hauptman matrix of a set of unitary structure factors 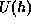 can be defined as follows,
can be defined as follows,
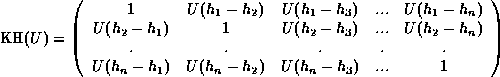
or,
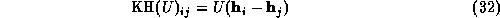
where 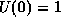 , and conventionally
, and conventionally 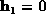 .
.
Consider the product of two Karle-Hauptman matrices of 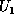 and
and
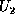 , where
, where 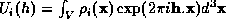 .
.
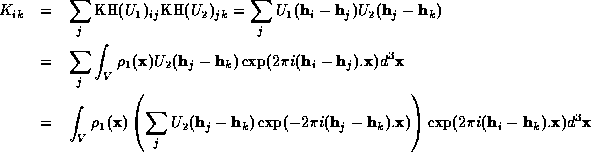
If enough reflections are included in the Karle-Hauptman determinant, the
summation over 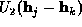 becomes the Fourier inversion formula
for
becomes the Fourier inversion formula
for 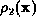 , thus:
, thus:
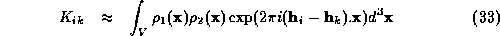
If 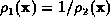 , then:
, then:
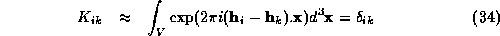
i.e. 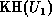 is the inverse of
is the inverse of 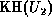 . Thus, if enough terms
are included, the Karle-Hauptman matrix associated with the inverse of
an electron density function is the inverse of the Karle-Hauptman
matrix associated with the electron density function itself.
. Thus, if enough terms
are included, the Karle-Hauptman matrix associated with the inverse of
an electron density function is the inverse of the Karle-Hauptman
matrix associated with the electron density function itself.